Researchers are figuring out how large language models work
Such insights could help make them safer, more truthful and easier to use

TO MOST PEOPLE, the inner workings of a car engine or a computer are a mystery. It might as well be a black box: never mind what goes on inside, as long as it works. Besides, the people who design and build such complex systems know how they work in great detail, and can diagnose and fix them when they go wrong. But that is not the case for large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, Claude and Gemini, which are at the forefront of the boom in artificial intelligence (AI).
LLMs are built using a technique called deep learning, in which a network of billions of neurons, simulated in software and modelled on the structure of the human brain, is exposed to trillions of examples of something to discover inherent patterns. Trained on text strings, LLMs can hold conversations, generate text in a variety of styles, write software code, translate between languages and more besides.
Explore more
This article appeared in the Science & technology section of the print edition under the headline “Inside the mind of an AI”
More from Science and technology

How Ukraine’s new tech foils Russian aerial attacks
It is pioneering acoustic detection, with surprising success

The deep sea is home to “dark oxygen”
Nodules on the seabed, rather than photosynthesis, are the source of the gas
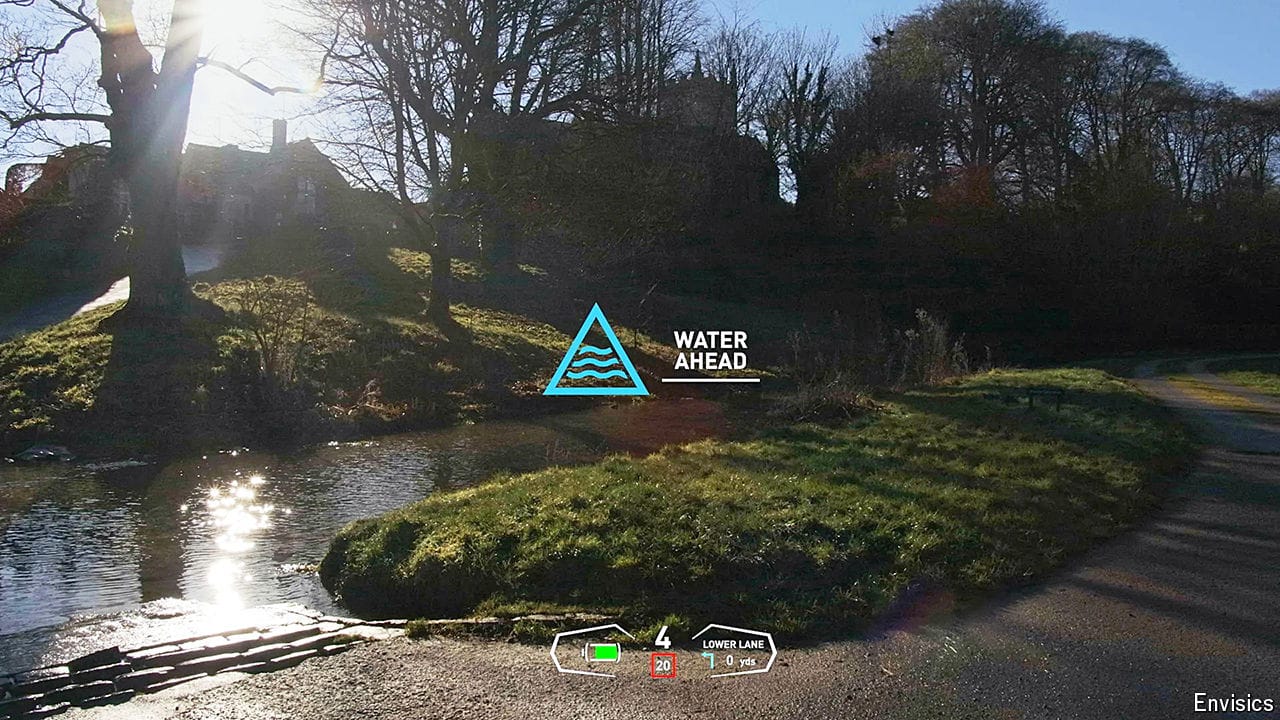
Augmented reality offers a safer driving experience
Complete with holograms on the windscreen
Clues to a possible cure for AIDS
Doctors, scientists and activists meet to discuss how to pummel HIV
AI can predict tipping points before they happen
Potential applications span from economics to epidemiology
Astronomers have found a cave on the moon
Such structures could serve as habitats for future astronauts
