America’s banks are more exposed to a downturn than they appear
To understand why, consider the ouroboros theory of financial risk

The earliest depiction of the ouroboros—a serpent coiled in a circle, eating its own tail—was found in the tomb of Tutankhamun, a pharaoh who ruled Egypt around 1320BC. It was used in his funerary texts to depict the infinite nature of time, and later cropped up all over the place. In Ancient Rome it signified the seasonal cycle of the calendar year; in Norse mythology the snake was large enough to encircle the world. The idea is also an allegory for the modern financial system. It depicts how credit risk has been cycled out of banks, only to be gobbled up by them once more.
Explore more
This article appeared in the Finance & economics section of the print edition under the headline “Ouroboros theory”
Finance & economics July 6th 2024
More from Finance and economics
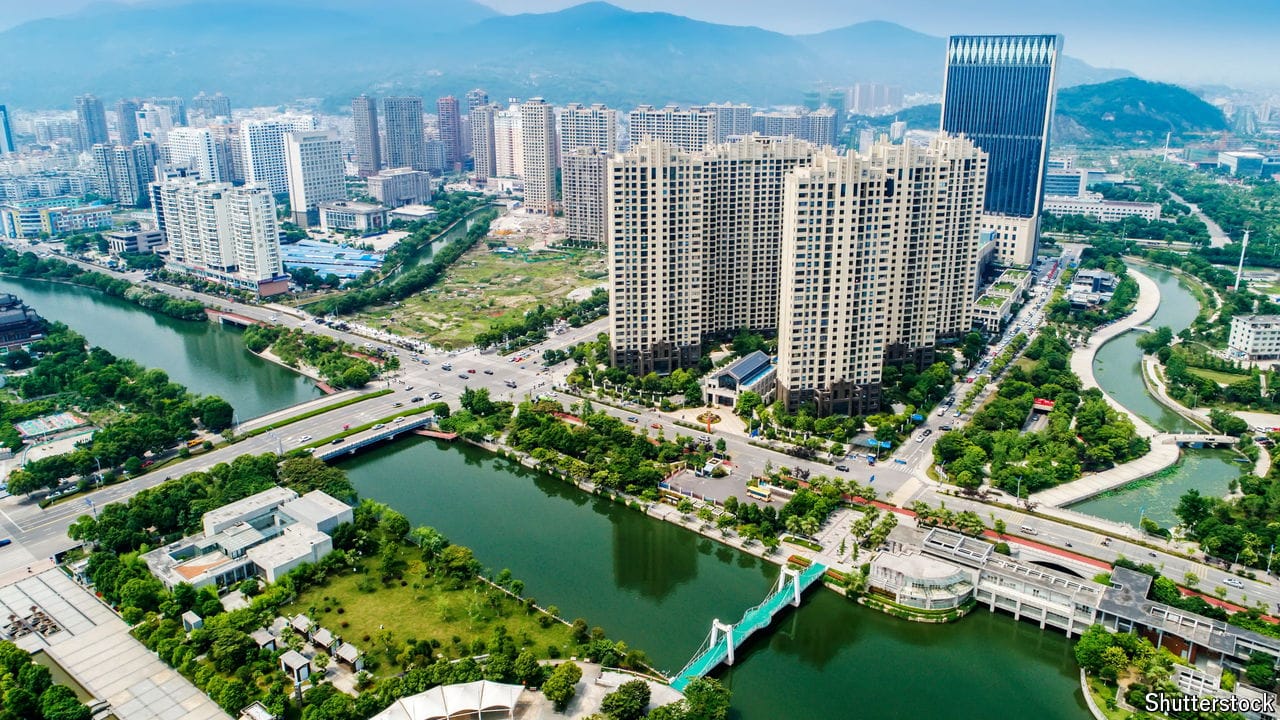

China’s last boomtowns show rapid growth is still possible
All it takes is for the state to work with the market
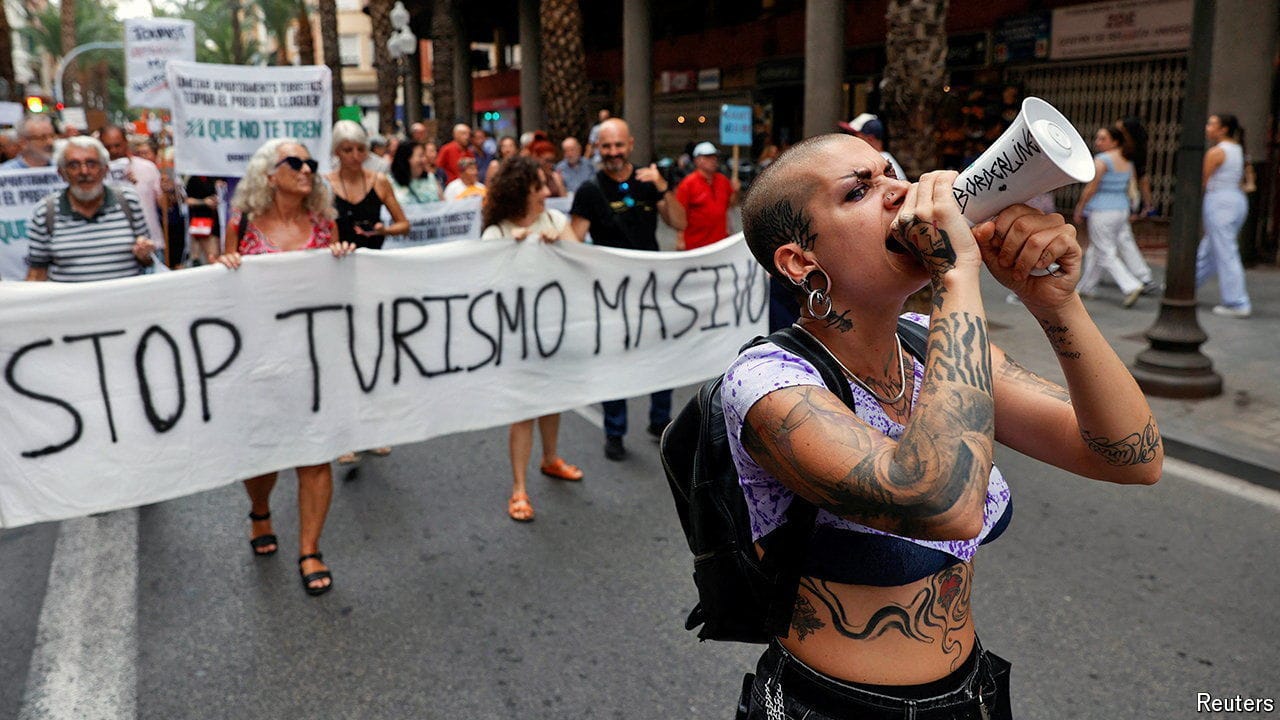

What the war on tourism gets wrong
Visitors are a boon, if managed wisely
Why investors are unwise to bet on elections
Turning a profit from political news is a lot harder than it looks
Revisiting the work of Donald Harris, father of Kamala
The combative Marxist economist focused on questions related to growth
Donald Trump wants a weaker dollar. What are his options?
All come with their own drawbacks
Why is Xi Jinping building secret commodity stockpiles?
Vast new holdings of grain, natural gas and oil suggest trouble ahead
