An incurable disease
A new book explains how health care can become both more expensive and more affordable
HEALTH-CARE expenditure in America is growing at a disturbing rate: in 1960 it was just over 5% of GDP, in 2011 almost 18%. By 2105 the number could reach 60%, according to William Baumol of New York University’s Stern School of Business. Incredible? It is simply the result of extrapolating the impact of a phenomenon Mr Baumol has become famous for identifying: “cost disease”. His new book* gives a nuanced diagnosis, offerings both a vision of a high-cost future and a large dose of optimism. The cost disease may be incurable, but it is also survivable—if treated correctly.
To understand the cost disease, start with a simple observation: whatever the economy’s average rate of productivity growth, some industries outpace others. Take car manufacturing. In 1913 Ford introduced assembly lines to move cars between workstations. This allowed workers, and their tools, to stay in one place, which cut the time to build a Model T car from 12 hours to less than two. As output per worker grows in such “progressive” sectors, firms can afford to increase wages.
This article appeared in the Finance & economics section of the print edition under the headline “An incurable disease”
More from Finance and economics
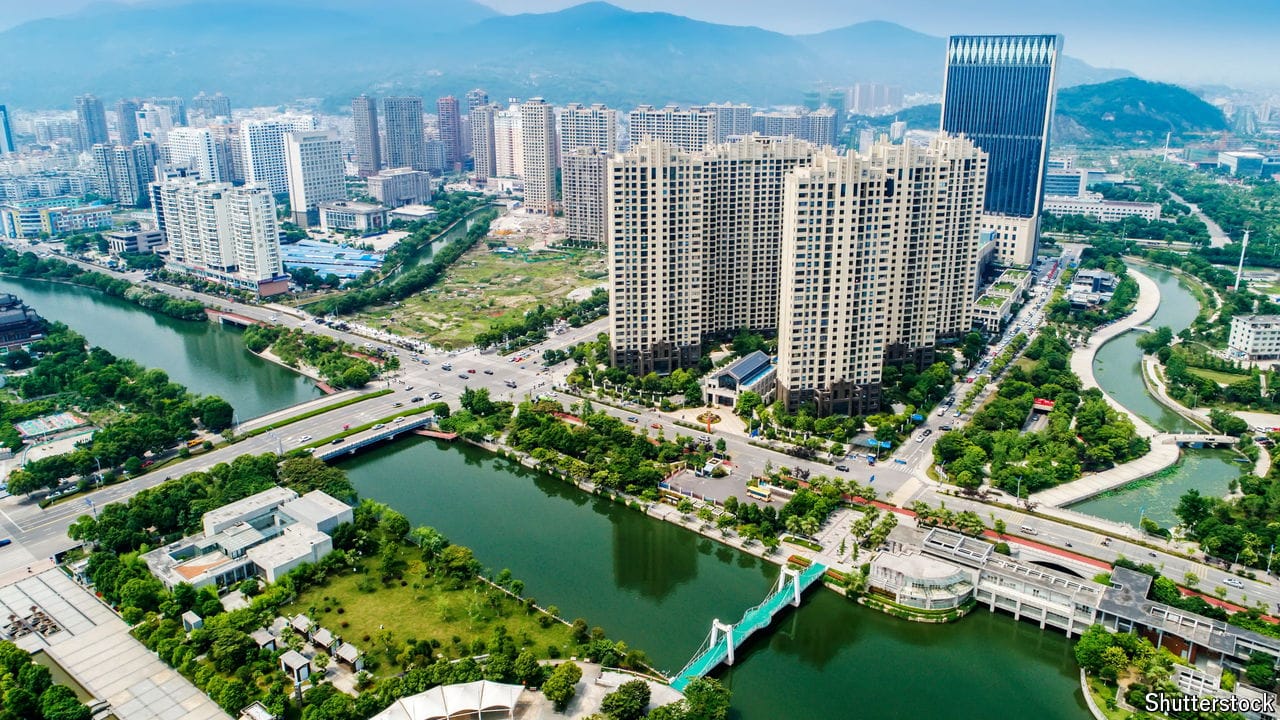

China’s last boomtowns show rapid growth is still possible
All it takes is for the state to work with the market
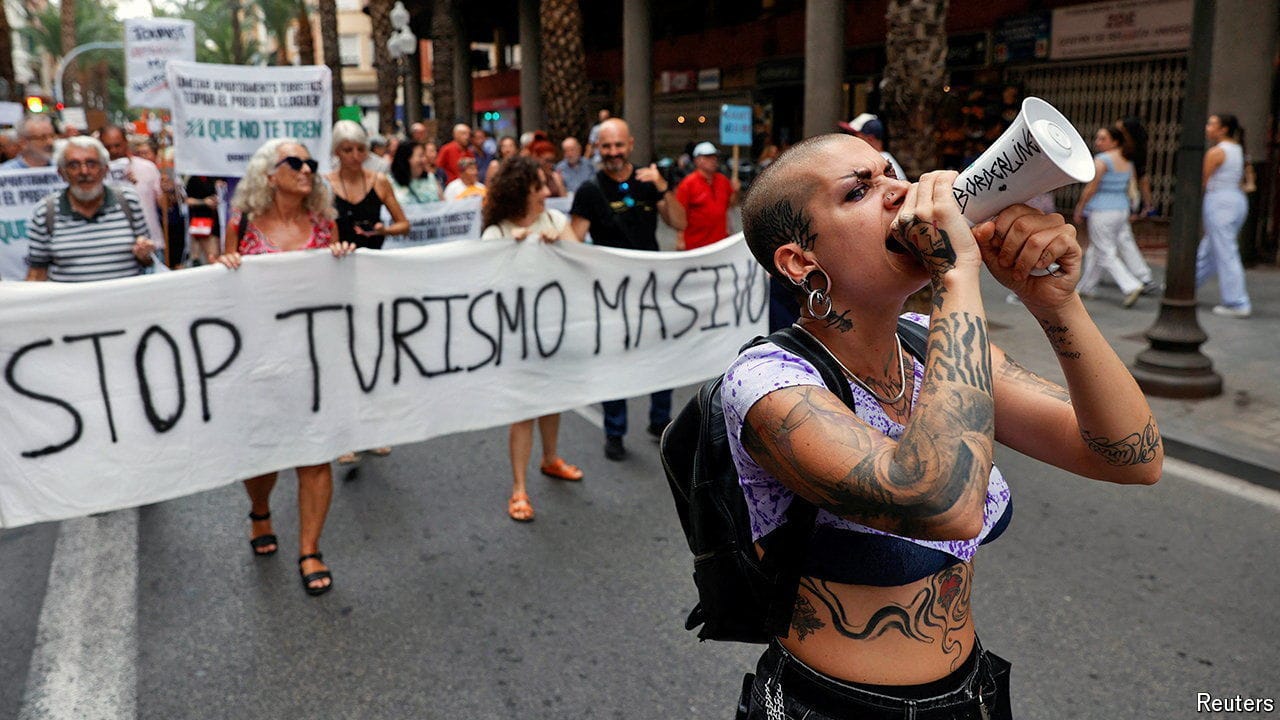

What the war on tourism gets wrong
Visitors are a boon, if managed wisely
Why investors are unwise to bet on elections
Turning a profit from political news is a lot harder than it looks
Revisiting the work of Donald Harris, father of Kamala
The combative Marxist economist focused on questions related to growth
Donald Trump wants a weaker dollar. What are his options?
All come with their own drawbacks
Why is Xi Jinping building secret commodity stockpiles?
Vast new holdings of grain, natural gas and oil suggest trouble ahead
