A new age of sail begins
By harnessing wind power, high-tech sails can help cut marine pollution

In 1926 an unusual vessel arrived in New York after crossing the Atlantic. This was a converted sailing ship renamed Baden-Baden. Its two masts had been torn down and a pair of 15-metre-high revolving cylinders were mounted on its deck instead. Known as Flettner rotors, after Anton Flettner, their German inventor, the rotors worked like sails. Not only were they extremely efficient, allowing the vessel to consume less than half the fuel an oil-powered ship of a similar size would use, they also let the craft tack closer to an oncoming wind than its original canvas rigging allowed. The rotors were hailed as a great achievement at the time (praised by Albert Einstein, among others) before cheap oil caused interest to wane.
This article appeared in the Science & technology section of the print edition under the headline “The second age of sail”
More from Science and technology
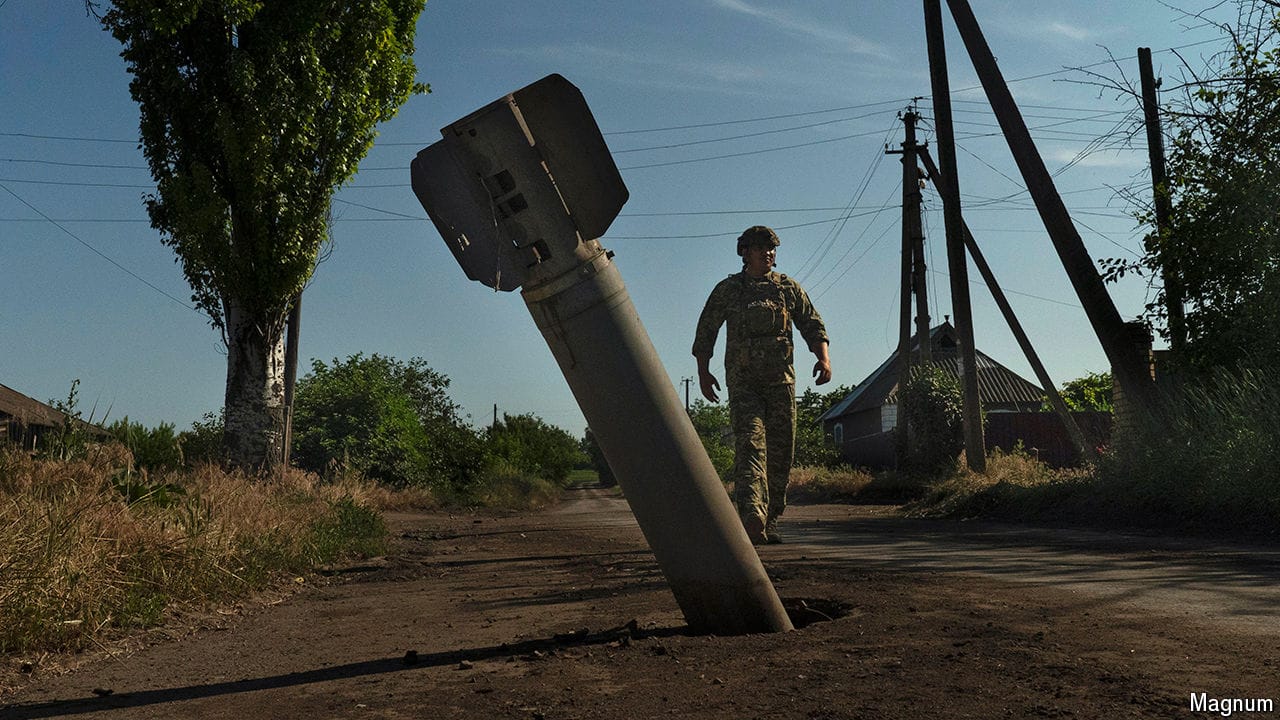

How Ukraine’s new tech foils Russian aerial attacks
It is pioneering acoustic detection, with surprising success
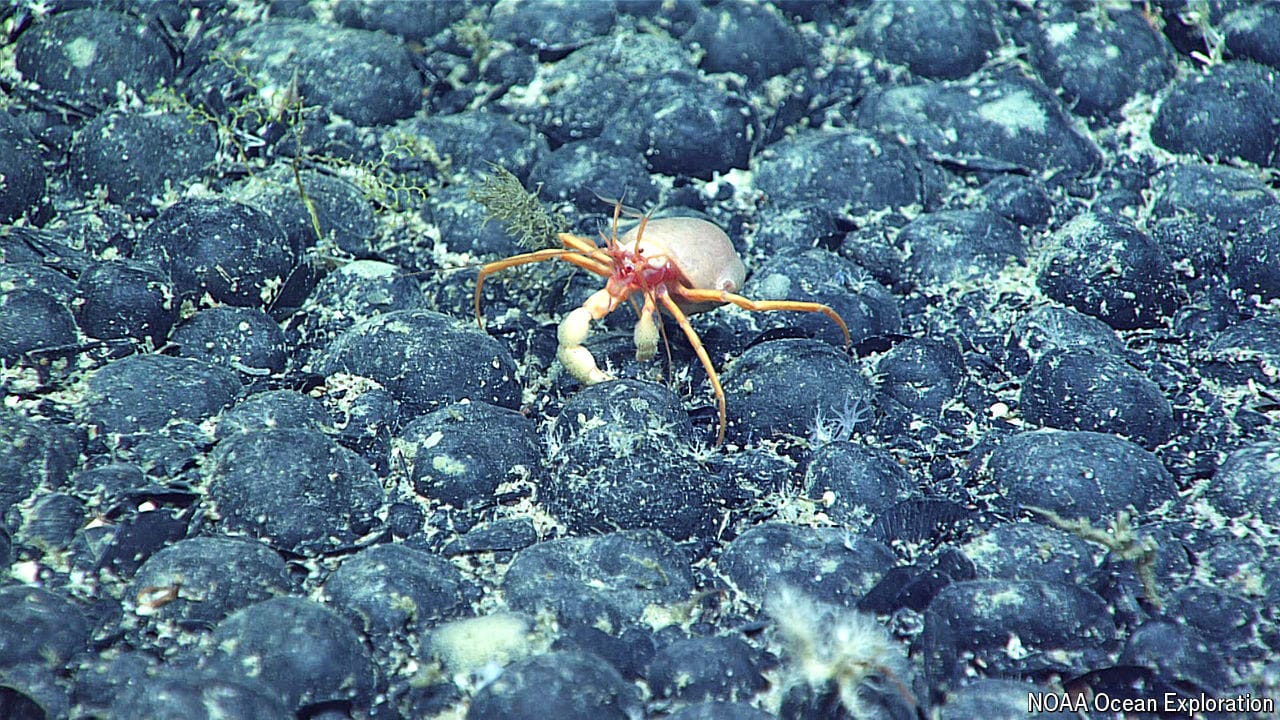

The deep sea is home to “dark oxygen”
Nodules on the seabed, rather than photosynthesis, are the source of the gas
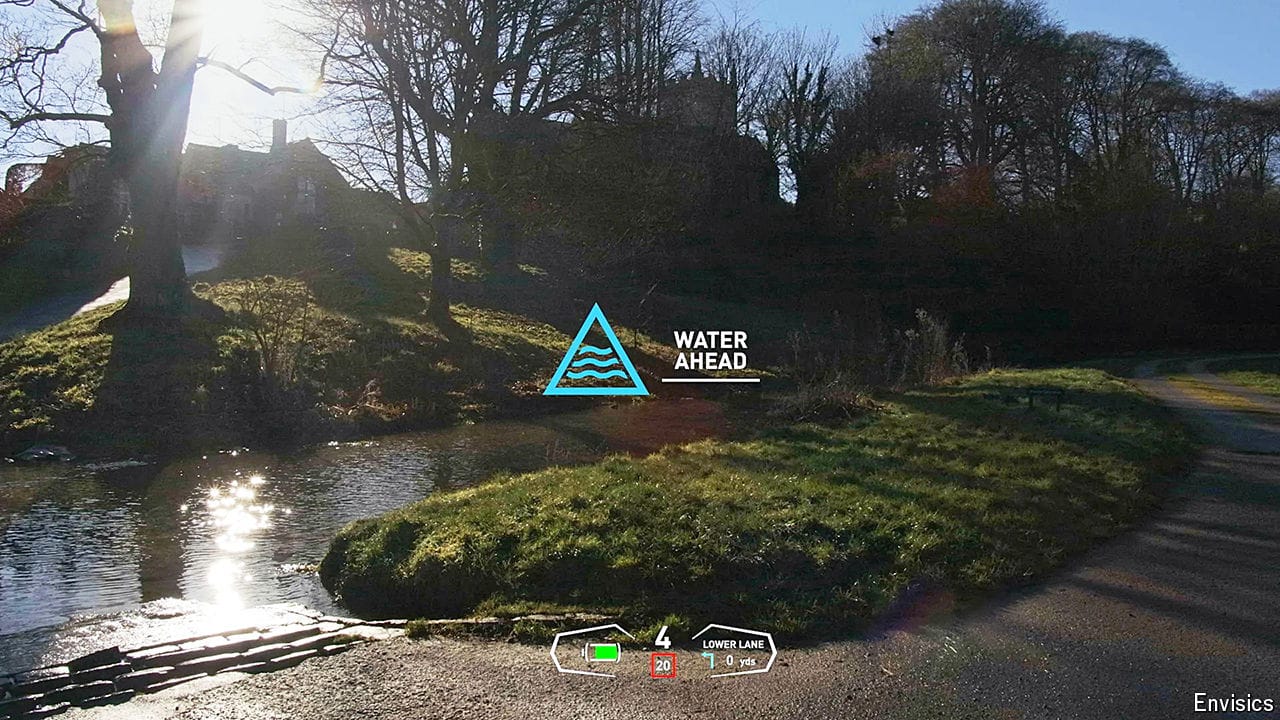
Augmented reality offers a safer driving experience
Complete with holograms on the windscreen
Clues to a possible cure for AIDS
Doctors, scientists and activists meet to discuss how to pummel HIV
AI can predict tipping points before they happen
Potential applications span from economics to epidemiology
Astronomers have found a cave on the moon
Such structures could serve as habitats for future astronauts
