Fighting in the Sahel has forced 1.7m people from their homes
Jihadists are only partly to blame
WESTERN GOVERNMENTS have long debated whether the costs of intervening in dangerous parts of the world exceed the risks. In February the United States signed a peace deal with the Taliban in Afghanistan. But just as America extricates itself from one conflict, a power vacuum in Africa’s Sahel may drag it into another.
The Sahel, a semi-arid strip south of the Sahara desert spanning 4,000 miles (6,400km), is unusually troubled. Its hinterlands are far from any city and mainly populated by nomads. The state’s writ does not hold; public services barely exist. The Sahel’s borderlands have long been dangerous: just 3.5% of the population of north and west Africa lives within 10km of an international frontier, but 10% of deaths from armed violence occurred in these areas between 1997 and 2019.
This article appeared in the Graphic detail section of the print edition under the headline “The next Afghanistan?”
More from Graphic detail
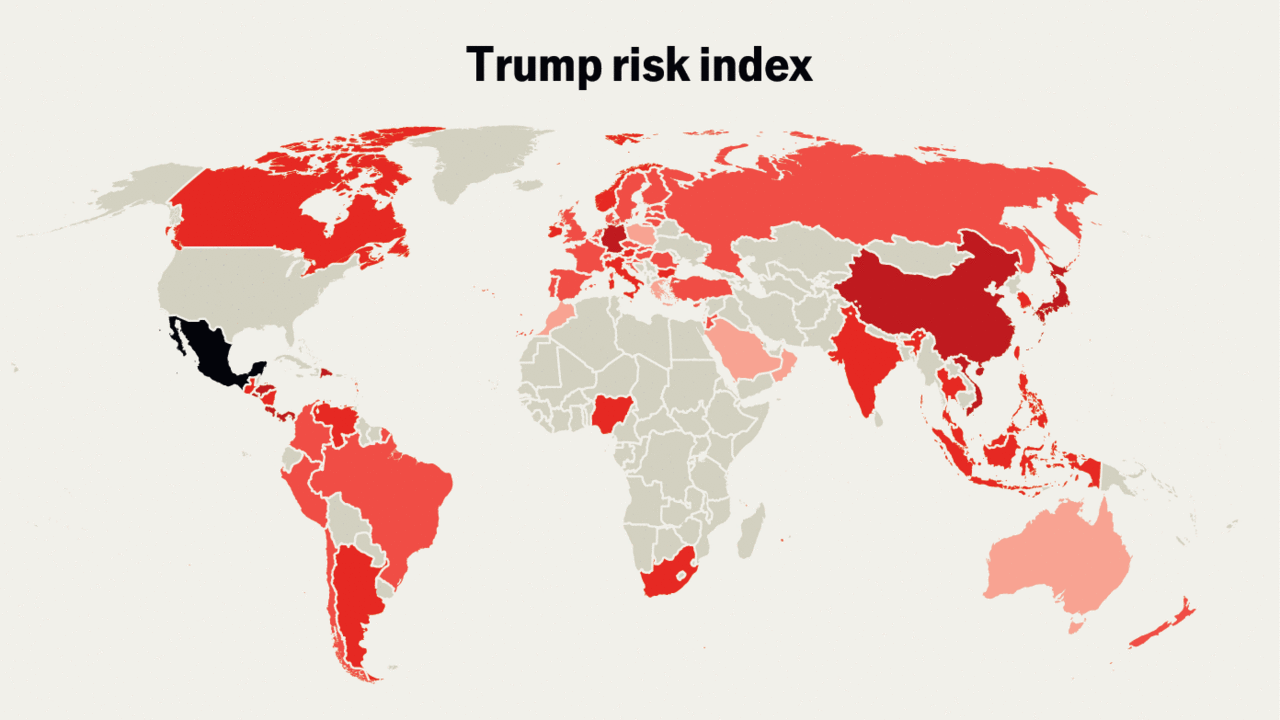
Which countries would be most affected by a second Trump term?
A ranking of America’s 70 largest trading partners

How long would it take to read the greatest books of all time?
The Economist consulted bibliophile data scientists to bring you the answer
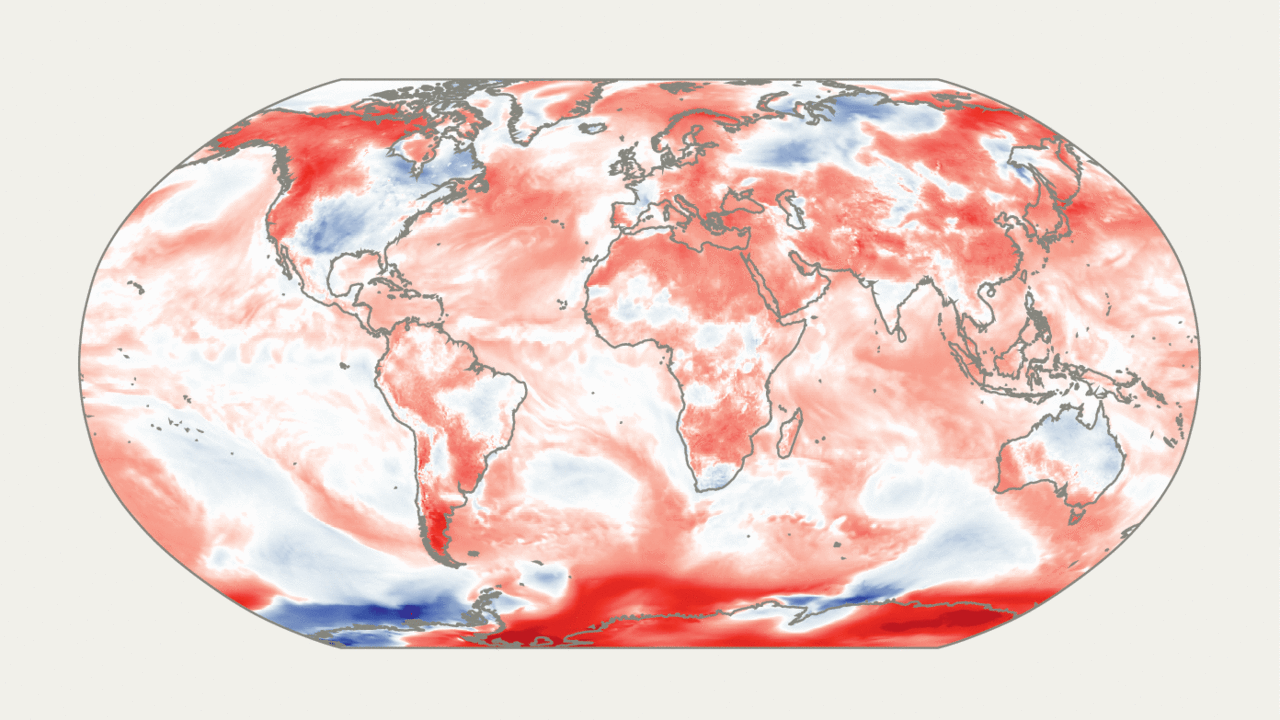
Why 2024 could become the hottest year on record
Global temperatures reach record highs twice in less than a week
Donald Trump is now the oldest candidate to run for president
But America’s issue with ageing politicians goes beyond the White House
Which country has the most Olympic medals?
One dominates. But a tiny island shows there are numerous ways to measure sporting prowess
Can America afford its debts?
Public debt stands at 98% of GDP. Neither Democrats nor Republicans are helping
